StatefulSet
StatefulSet
Why We Need StatefulSets?
All pods under a Deployment have the same characteristics except for the name and IP address.
If required, a Deployment can use the pod template to create a new pod.
If not required, the Deployment can delete any one of the pods.
However, Deployments cannot meet the requirements in some distributed scenarios when each pod requires its own status
or in a distributed database where each pod requires independent storage.
With detailed analysis, it is found that each part of distributed stateful applications plays a different role (or different responsibility). For example, the database nodes are deployed in active/standby mode, and pods are dependent on each other. To be specific, the pods in Kubernetes must meet the following requirements:
A pod can be recognized by other pods. Therefore, a pod must have a fixed identifier. Each pod has an independent
storage device. After a pod is deleted and then restored, the data read from the pod must be the same as the previous
one. Otherwise, the pod status is inconsistent. To address the preceding requirements, Kubernetes provides
StatefulSets.
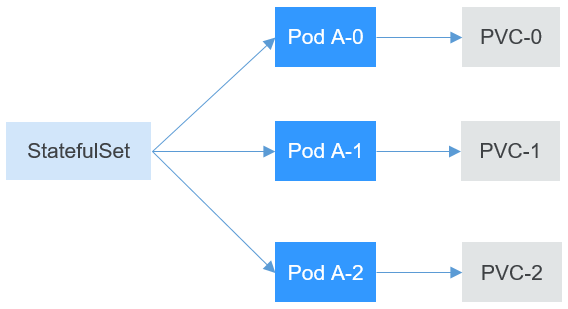
A StatefulSet provides a fixed name for each pod following a fixed number ranging from 0 to N. After a pod is
rescheduled, the pod name and the host name remain unchanged. The StatefulSet provides a fixed access domain name for
each pod through the headless Service. For details about the Service, see Services. The StatefulSet creates
PersistentVolumeClaims (PVCs) with fixed identifiers to ensure that pods can access the same persistent data after
being rescheduled.
The following describes how to create a StatefulSet and experience its features.
Create Namespace and change context
Begin by creating a namespace:
kubectl create namespace statefulset01
namespace/statefulset01 created
Let’s change the context
kubectl config set-context --current --namespace statefulset01
Context "xxxxx@xxxxxx" modified.
Create ClusterIP headless Service
A headless Service is required for pod access when a StatefulSet is created.
Use the following file to describe the headless Service:
spec.clusterIP: Set it toNone, which indicates a headlessServiceis to be created.spec.ports.port: indicates the number of the port for communication between pods.spec.ports.name: indicates the name of the port used for communication between pods.
The headless service will permit you to resolve directly the IP address of the POD when you wants to resolve the name of the service:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service # The object type is Service.
metadata:
name: headless-svc
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
ports:
- name: nginx # Name of the port for communication between pods
port: 80 # Number of the port for communication between pods
selector:
app: nginx # Select the pod whose label is app:nginx.
clusterIP: None # Set this parameter to None, indicating that a headless Service is to be created.
Run the following command to create a headless Service:
kubectl apply -f statefulset-headless.yaml
service/headless-svc created
After the Service is created, you can query the Service information.
kubectl get svc
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE headless-svc ClusterIP None <none> 80/TCP 22s
Creating a StatefulSet
The YAML definition of StatefulSets is basically the same as that of other objects. The differences are as follows:
serviceNamespecifies the headless Service used by the StatefulSet. You need to specify the name of the headless service.volumeClaimTemplatesis used to apply for a PVC . A template named data is defined, which will create a PVC for each pod.storageClassNamespecifies the persistent storage class. For details, see PersistentVolumes, PersistentVolumeClaims, and StorageClasses.volumeMountsis used to mount storage to pods. If no storage is required, you can delete thevolumeClaimTemplatesandvolumeMountsfields.
Check the StorageClass in your cluster:
kubectl get sc
NAME PROVISIONER RECLAIMPOLICY VOLUMEBINDINGMODE ALLOWVOLUMEEXPANSION AGE nfs-storageclass (default) nfs-deso-provisioner Delete Immediate false 75d
In our cluster we have nfs-storageclass. If you StorageClass is different please note it.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: StatefulSet
metadata:
name: statefulset-nginx
spec:
serviceName: headless-svc # Name of the headless Service
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: container-0
image: r.deso.tech/library/nginx
resources:
limits:
cpu: 100m
memory: 200Mi
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 200Mi
volumeMounts: # Storage mounted to the pod
- name: data
mountPath: /usr/share/nginx/html # Mount the storage to /usr/share/nginx/html.
imagePullSecrets:
- name: default-secret
volumeClaimTemplates:
- metadata:
name: data
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
storageClassName: nfs-storageclass # Insert Storage class for Persistent storage class
Check your PersistentVolume:
kubectl get pv,pvc
No resources found
Run the following command to create a StatefulSet:
kubectl apply -f statefulset-nginx.yaml && kubectl get pod -w
statefulset.apps/statefulset-nginx created
After the command is executed, query the StatefulSet and pods. The suffix of the pod names starts from 0 and increases to 2.
kubectl apply -f statefulset-nginx.yaml && kubectl get pod -w
statefulset.apps/statefulset-nginx created NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE statefulset-nginx-0 0/1 Pending 0 0s statefulset-nginx-0 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s statefulset-nginx-0 1/1 Running 0 4s statefulset-nginx-1 0/1 Pending 0 0s statefulset-nginx-1 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 2s statefulset-nginx-1 1/1 Running 0 4s statefulset-nginx-2 0/1 Pending 0 0s statefulset-nginx-2 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 2s statefulset-nginx-2 1/1 Running 0 4s
kubectl get statefulset
NAME READY AGE statefulset-nginx 3/3 74s
In this case, if you manually delete the nginx-1 pod and query the pods again, you can see that a pod with the same
name is created.
kubectl delete pod statefulset-nginx-1
pod "statefulset-nginx-1" deleted
kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE statefulset-nginx-0 1/1 Running 0 2m32s statefulset-nginx-1 1/1 Running 0 6s statefulset-nginx-2 1/1 Running 0 2m24s
According to 6s under AGE, it is found that the statefulset-nginx-1 pod is newly created.
Access the container and check its host names.
The host names are statefulset-nginx-0, statefulset-nginx-1, and statefulset-nginx-2.
kubectl exec statefulset-nginx-0 -- sh -c 'hostname'
statefulset-nginx-0
kubectl exec statefulset-nginx-1 -- sh -c 'hostname'
statefulset-nginx-1
kubectl exec statefulset-nginx-2 -- sh -c 'hostname'
statefulset-nginx-2
In addition, you can view the PVCs created by the StatefulSet.
These PVCs are named in the format of PVC name-StatefulSet name-No. and are in the Bound state.
kubectl get pvc
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE data-statefulset-nginx-0 Bound pvc-4d746f81-e9a9-4804-8ec7-a113c75524b1 1Gi RWX nfs-storageclass 7m38s data-statefulset-nginx-1 Bound pvc-73722e46-a3f4-4d72-a50d-71fc40f3d9e7 1Gi RWX nfs-storageclass 6m6s data-statefulset-nginx-2 Bound pvc-afeadadc-2120-4096-b5da-da1c6a7915ab 1Gi RWX nfs-storageclass 5m59s
kubectl get pv
NAME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES RECLAIM POLICY STATUS CLAIM STORAGECLASS REASON AGE pvc-4d746f81-e9a9-4804-8ec7-a113c75524b1 1Gi RWX Delete Bound statefulset/data-statefulset-nginx-0 nfs-storageclass 7m53s pvc-73722e46-a3f4-4d72-a50d-71fc40f3d9e7 1Gi RWX Delete Bound statefulset/data-statefulset-nginx-1 nfs-storageclass 6m21s pvc-afeadadc-2120-4096-b5da-da1c6a7915ab 1Gi RWX Delete Bound statefulset/data-statefulset-nginx-2 nfs-storageclass 6m14s
Network Identifier of a StatefulSet
After a StatefulSet is created, you can see that each pod has a fixed name.
The headless Service provides a fixed domain name for pods by using DNS.
In this way, pods can be accessed using the domain name.
Even if the IP address of the pod changes when the pod is re-created, the domain name remains unchanged.
After a headless Service is created, the IP address of each pod corresponds to a domain name in the following format:
<pod-name>.<svc-name>.<namespace>.svc.cluster.local
For example, the domain names of the three pods are as follows:
statefulset-nginx-0.headless-svc.statefulset.svc.cluster.localstatefulset-nginx-1.headless-svc.statefulset.svc.cluster.localstatefulset-nginx-2.headless-svc.statefulset.svc.cluster.local
When accessing it, .<namespace>.svc.cluster.local can actually be omitted.
The name of the cluster can change based on your cluster.
Create a pod from the netshoot image. Then, access the container of the pod and run the nslookup command to view
the domain name of the pod. The IP address of the pod can be parsed. The IP address of the DNS server is 10.96.0.10.
When a kubernetes cluster is created, the coredns add-on is installed by default to provide the DNS service.
kubectl run -i --tty --image r.deso.tech/library/netshoot testdns --restart=Never --rm /bin/bash
If you don't see a command prompt, try pressing enter. bash-5.0#
nslookup headless-svc
Server: 10.96.0.10 Address: 10.96.0.10#53 Name: headless-svc.statefulset.svc.desocluster.local Address: 192.168.69.223 Name: headless-svc.statefulset.svc.desocluster.local Address: 192.168.39.217 Name: headless-svc.statefulset.svc.desocluster.local Address: 192.168.79.79
nslookup statefulset-nginx-0.headless-svc
Server: 10.96.0.10 Address: 10.96.0.10#53 Name: statefulset-nginx-0.headless-svc.statefulset.svc.desocluster.local Address: 192.168.79.79
nslookup statefulset-nginx-1.headless-svc
Server: 10.96.0.10 Address: 10.96.0.10#53 Name: statefulset-nginx-1.headless-svc.statefulset.svc.desocluster.local Address: 192.168.69.223
nslookup statefulset-nginx-2.headless-svc
Server: 10.96.0.10 Address: 10.96.0.10#53 Name: statefulset-nginx-2.headless-svc.statefulset.svc.desocluster.local Address: 192.168.39.217
exit
If you manually delete one of the pods, query the IP addresses of the pods re-created by the StatefulSet, and run the
nslookup command to parse the domain names of the pods, you can find that statefulset-nginx-0,statefulset-nginx-1
and statefulset-nginx-2 are parsed to the corresponding pods. This ensures that the network identifier of the
StatefulSet remains unchanged.
kubectl get pod -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES statefulset-nginx-0 1/1 Running 0 17m 192.168.79.79 k8s-worker01 <none> <none> statefulset-nginx-1 1/1 Running 0 15m 192.168.69.223 k8s-worker02 <none> <none> statefulset-nginx-2 1/1 Running 0 17m 192.168.39.217 k8s-worker03 <none> <none>
kubectl delete pod statefulset-nginx-0
pod "statefulset-nginx-0" deleted
kubectl get pod -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES statefulset-nginx-0 1/1 Running 0 31s 192.168.79.77 k8s-worker01 <none> <none> statefulset-nginx-1 1/1 Running 0 18m 192.168.69.223 k8s-worker02 <none> <none> statefulset-nginx-2 1/1 Running 0 21m 192.168.39.217 k8s-worker03 <none> <none>
Note the IP address of the pod statefulset-nginx-0 is changed. Run the netshoot container again:
kubectl run -i --tty --image r.deso.tech/library/netshoot testdns1 --restart=Never --rm /bin/bash
If you don't see a command prompt, try pressing enter. bash-5.0#
nslookup statefulset-nginx-0.headless-svc
Server: 10.96.0.10 Address: 10.96.0.10#53 Name: statefulset-nginx-0.headless-svc.statefulset.svc.desocluster.local Address: 192.168.79.77
The new IP address come out. Automatic domain name resolution.
StatefulSet Storage Status
As mentioned above, StatefulSets can use PVCs for persistent storage to ensure that the same persistent data can be
accessed after pods are rescheduled. When pods are deleted, PVCs are not deleted.

Run the following command to write some data into the /usr/share/nginx/html directory of statefulset-nginx-1.
For example, change the content of index.html to hello Desotech Student.
kubectl exec statefulset-nginx-1 -- sh -c 'echo hello Desotech Student > /usr/share/nginx/html/index.html'
After the modification, if you access https://localhost, hello Desotech Student is returned.
kubectl exec -it statefulset-nginx-1 -- curl localhost
hello Desotech Student
In this case, if you manually delete the statefulset-nginx-1 pod and query the pod again, you can see that a pod with
the same name is created.
kubectl delete pod statefulset-nginx-1
pod "statefulset-nginx-1" deleted
kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE statefulset-nginx-0 1/1 Running 0 7m4s statefulset-nginx-1 1/1 Running 0 9s statefulset-nginx-2 1/1 Running 0 27m
According to 9s under AGE, it is found that the statefulset-nginx-1 pod is newly created.
Access the index.html page of the pod again. hello Desotech Student is still returned, which indicates that the pod
still accesses the same storage.
kubectl exec -it statefulset-nginx-1 -- curl localhost
hello Desotech Student